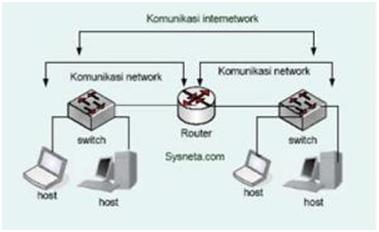
Tanggal Praktikum : 27 April 2010
lab2@lab2-desktop:~$ sudo su
[sudo] password for lab2:
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# lspci
00:00.0 Host bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 Host Bridge
00:00.1 Host bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 Host Bridge
00:00.2 Host bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 Host Bridge
00:00.3 Host bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 Host Bridge
00:00.4 Host bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 Host Bridge
00:00.5 PIC: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 I/O APIC Interrupt Controller
00:00.6 Host bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 Security Device
00:00.7 Host bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 Host Bridge
00:01.0 PCI bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT8237/VX700 PCI Bridge
00:02.0 PCI bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 PCI to PCI Bridge Controller
00:03.0 PCI bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 PCI to PCI Bridge Controller
00:0f.0 IDE interface: VIA Technologies, Inc. Device 5337 (rev 80)
00:0f.1 IDE interface: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT82C586A/B/VT82C686/A/B/VT823x/A/C PIPC Bus Master IDE (rev 07)
00:10.0 USB Controller: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT82xxxxx UHCI USB 1.1 Controller (rev a0)
00:10.1 USB Controller: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT82xxxxx UHCI USB 1.1 Controller (rev a0)
00:10.2 USB Controller: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT82xxxxx UHCI USB 1.1 Controller (rev a0)
00:10.3 USB Controller: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT82xxxxx UHCI USB 1.1 Controller (rev a0)
00:10.4 USB Controller: VIA Technologies, Inc. USB 2.0 (rev 86)
00:11.0 ISA bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT8237A PCI to ISA Bridge
00:11.7 Host bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT8251 Ultra VLINK Controller
00:12.0 Ethernet controller: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT6102 [Rhine-II] (rev 7c)
00:13.0 Host bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT8237A Host Bridge
00:13.1 PCI bridge: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT8237A PCI to PCI Bridge
01:00.0 VGA compatible controller: VIA Technologies, Inc. P4M890 [S3 UniChrome Pro] (rev 01)
04:03.0 Ethernet controller: 3Com Corporation 3c905B 100BaseTX [Cyclone]
80:01.0 Audio device: VIA Technologies, Inc. VT1708/A [Azalia HDAC] (VIA High Definition Audio Controller) (rev 10)
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ifconfig eth0 192.168.0.254
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ifconfig eth1 10.255.255.254
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:e0:4d:3d:8c:c2
inet addr:192.168.0.254 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
Interrupt:23 Base address:0x4000
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:4b:66:ca:49
inet addr:10.255.255.254 Bcast:10.255.255.255 Mask:255.0.0.0
UP BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
Interrupt:16 Base address:0x8000
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB) TX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB)
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# mii-tool
eth0: no link
eth1: no link
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ping 10.0.0.1
PING 10.0.0.1 (10.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.898 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.097 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.107 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.105 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.098 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.091 ms
^C
--- 10.0.0.1 ping statistics ---
6 packets transmitted, 6 received, 0% packet loss, time 5004ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.091/0.232/0.898/0.298 ms
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ping 192.168.0.1
PING 192.168.0.1 (192.168.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=3.92 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.098 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.093 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.100 ms
^C
--- 192.168.0.1 ping statistics ---
4 packets transmitted, 4 received, 0% packet loss, time 3007ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.093/1.053/3.921/1.655 ms
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:e0:4d:3d:8c:c2
inet addr:192.168.0.254 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::2e0:4dff:fe3d:8cc2/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:23 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:28 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:3462 (3.4 KB) TX bytes:3558 (3.5 KB)
Interrupt:23 Base address:0x4000
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:4b:66:ca:49
inet6 addr: fe80::210:4bff:fe66:ca49/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:76 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:54 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:10944 (10.9 KB) TX bytes:8897 (8.8 KB)
Interrupt:16 Base address:0x8000
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB) TX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB)
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ifconfig eth1 10.255.255.254
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:e0:4d:3d:8c:c2
inet addr:192.168.0.254 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::2e0:4dff:fe3d:8cc2/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:25 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:31 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:4146 (4.1 KB) TX bytes:4584 (4.5 KB)
Interrupt:23 Base address:0x4000
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:4b:66:ca:49
inet addr:10.255.255.254 Bcast:10.255.255.255 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: fe80::210:4bff:fe66:ca49/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:76 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:62 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:10944 (10.9 KB) TX bytes:11117 (11.1 KB)
Interrupt:16 Base address:0x8000
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB) TX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB)
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ping 10.0.0.1
PING 10.0.0.1 (10.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.123 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.099 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.120 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.119 ms
^C
--- 10.0.0.1 ping statistics ---
4 packets transmitted, 4 received, 0% packet loss, time 2997ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.099/0.115/0.123/0.012 ms
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ping 192.168.0.1
PING 192.168.0.1 (192.168.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.506 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.098 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.097 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.091 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.100 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.082 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=7 ttl=64 time=0.098 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=8 ttl=64 time=0.100 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=9 ttl=64 time=0.099 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=10 ttl=64 time=0.094 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=11 ttl=64 time=0.113 ms
^C
--- 192.168.0.1 ping statistics ---
11 packets transmitted, 11 received, 0% packet loss, time 10000ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.082/0.134/0.506/0.118 ms
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# mii-tool
eth0: negotiated 100baseTx-FD, link ok
eth1: negotiated 100baseTx-FD, link ok
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# route add default gw 192.168.254
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# route add default gw 192.168.0.254
SIOCADDRT: File exists
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# route add default gw 10.255.255.254
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth1
0.0.0.0 10.255.255.254 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
0.0.0.0 192.168.0.254 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0 -d 0/0 -j MASQUERADE
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ping 192.168.0.1
PING 192.168.0.1 (192.168.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=2.69 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.142 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.134 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.138 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.136 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.116 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=7 ttl=64 time=0.134 ms
^C
--- 192.168.0.1 ping statistics ---
7 packets transmitted, 7 received, 0% packet loss, time 6006ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.116/0.498/2.692/0.895 ms
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ping 10.0.0.1
PING 10.0.0.1 (10.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=5.43 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.138 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.136 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.135 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.137 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.1: icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.123 ms
^C
--- 10.0.0.1 ping statistics ---
6 packets transmitted, 6 received, 0% packet loss, time 5005ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.123/1.017/5.433/1.974 ms
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:e0:4d:3d:8c:c2
inet addr:192.168.0.254 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::2e0:4dff:fe3d:8cc2/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:61 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:65 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:10938 (10.9 KB) TX bytes:10620 (10.6 KB)
Interrupt:23 Base address:0x4000
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:4b:66:ca:49
inet addr:10.255.255.254 Bcast:10.255.255.255 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: fe80::210:4bff:fe66:ca49/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:114 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:86 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:18664 (18.6 KB) TX bytes:13692 (13.6 KB)
Interrupt:16 Base address:0x8000
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB) TX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB)
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# mii-tool
eth0: negotiated 100baseTx-FD, link ok
eth1: negotiated 100baseTx-FD, link ok
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth1
0.0.0.0 10.255.255.254 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
0.0.0.0 192.168.0.254 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
root@lab2-desktop:/home/lab2# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:e0:4d:3d:8c:c2
inet addr:192.168.0.254 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::2e0:4dff:fe3d:8cc2/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:70 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:83 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:14016 (14.0 KB) TX bytes:16776 (16.7 KB)
Interrupt:23 Base address:0x4000
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:4b:66:ca:49
inet addr:10.255.255.254 Bcast:10.255.255.255 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: fe80::210:4bff:fe66:ca49/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:146 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:105 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:24896 (24.8 KB) TX bytes:15478 (15.4 KB)
Interrupt:16 Base address:0x8000
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:254 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB) TX bytes:18016 (18.0 KB)